Technical Guide: How to Choose M.2 Storage
Blog
Overview
Selecting the correct M.2 storage can be challenging due to the variety of types, sizes, and versions available. This guide explains the key characteristics of M.2 storage and provides a step-by-step process to ensure you choose the right one for your application.
Understanding M.2 Storage
M.2 is not just additional storage; it’s an expansion slot. Expansion slots allow you to connect cards to the computer that add functionality to it. For example, you can use an expansion slot to add a card to the computer that enables Wi-Fi or additional I/O.
M.2 stands out among storage and expansion technologies by combining multiple functionalities into one socket. For example, one M.2 slot can support several different types of technology such as USB, SATA and PCIe.
For this reason, M.2 slots come in many different sizes and versions.
M.2 Sizes
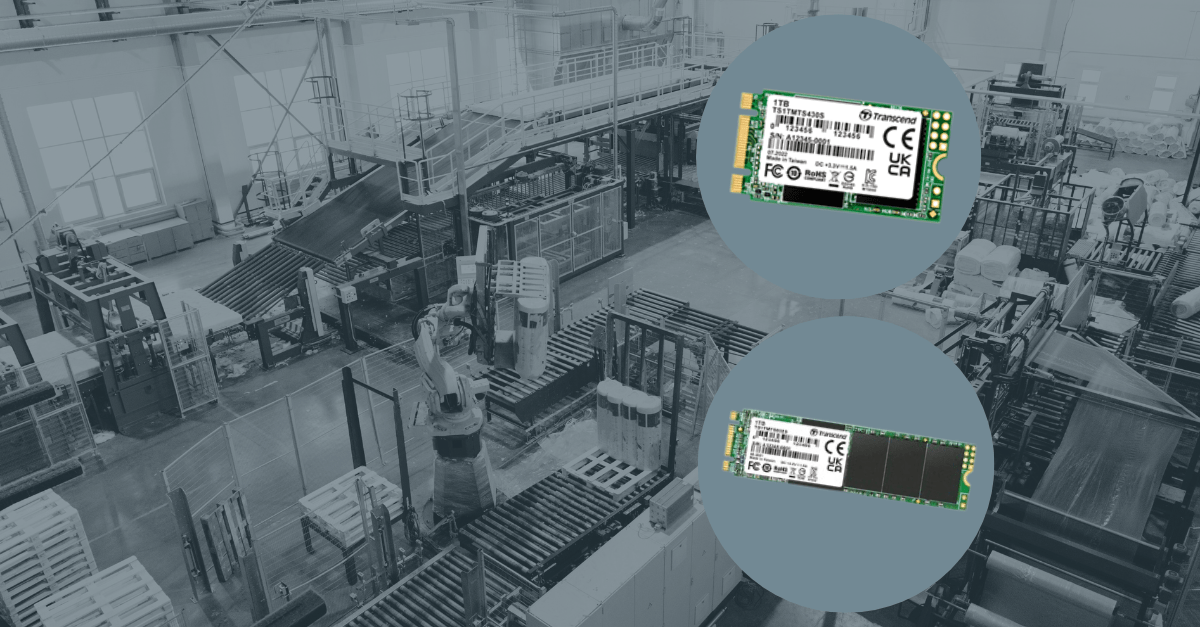
M.2 cards come in various sizes, labeled by their width and length. For example:
- 2280: 22 mm wide and 80 mm long
- 2230: 22 mm wide and 30 mm long
- 2242: 22 mm wide and 42 mm long
These are the most common sizes, and compatibility depends on the device and its motherboard specifications. 

2280 M.2 (top) vs. 2242 M.2 (bottom)
M.2 Versions (Keys)
M.2 cards and slots come in 13 different versions, and each version supports different storage/expansion technologies. These versions are called Keys because each version is physically different and has notches (gaps) in different locations to make sure that it will only fit in its own correct Key.
Common M.2 Keys:
- B Key:
-
- Supports SATA, PCIe x2, USB, and other expansions
-
- Typically used for simple expansion features like Wi-Fi and simple, slow storage
- M Key:
-
- Supports SATA, PCIe x4, and other expansions
-
- Designed for high-speed expansion and storage like NVMe
- B+M Key:
-
- Compatible with both B and M slots
-
- Supports SATA, PCIe x 2, and other expansions
Selecting the wrong Key will result in incompatibility, as the card will not fit the slot. Refer to your device’s datasheet to confirm the supported Key type.

Image: M.2 Edge Connector Keying by NikNaks, licensed under CC BY-SA 3.0.
Storage Interfaces*

*This chart has been simplified to include only storage interfaces. A full list of Key IDs is available here.
PCIe Technology and Lanes
PCIe (Peripheral Component Interconnect Express) is a high-speed expansion technology used for M.2 slots.
PCIe technology uses lanes to transfer data, with more lanes providing higher data rates. Another crucial element influencing speed is the generation of PCIe technology (e.g., PCIe 3.0 vs. PCIe 6.0).
For example:
- 1 lane of PCIe 3.0 (released in 2010) can transfer data at 1GB/s
- 1 lane of PCIe 4.0 (released in 2016) can transfer data at 2GB/s
The number of lanes is denoted by an “x” (e.g., x2 for 2 lanes, x4 for 4 lanes). The M.2 M Key can support up to 4 PCIe lanes, enabling speeds of 4-8 GB/s, which is 6 to 12 times faster than SATA technology.
NVMe Technology
NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) is a protocol designed for high-speed storage using PCIe.
- NVMe is non-volatile, meaning it retains data even when the power is off. As opposed to RAM, which is volatile and wipes with every reboot.
- It is currently the fastest computer storage technology and generally more expensive.
NVMe Compatibility:
- M Key: Supports NVMe x4 (PCIe x4)
- B Key: Supports NVMe x2 (PCIe x2), though B Key NVMe is rare. If offered to you, request documentation and images of the module to verify its Key.
Always verify compatibility with the motherboard’s datasheet, as some slots may not support NVMe, even if the Key matches.
Steps for Selecting an M.2
- Verify the M.2 Key required. Check the device or motherboard datasheet for supported Key types.
- Verify the M.2 size that is required. Ensure the dimensions match the available slot.
- Confirm NVMe compatibility. Use the datasheet to verify if the motherboard and Key type accept NVMe.
- Review the offerings. Review your options based on compatibility and project specifications.
- Verify the offerings. Verify that the parts being offered are the correct size and Key.
- Select the M.2 storage. Choose the part that meets all the above criteria.
Conclusion
Selecting the correct M.2 storage requires careful consideration of Key type, size, and compatibility with your motherboard and application requirements. Following this guide will help ensure a seamless selection process and optimal performance for your system.